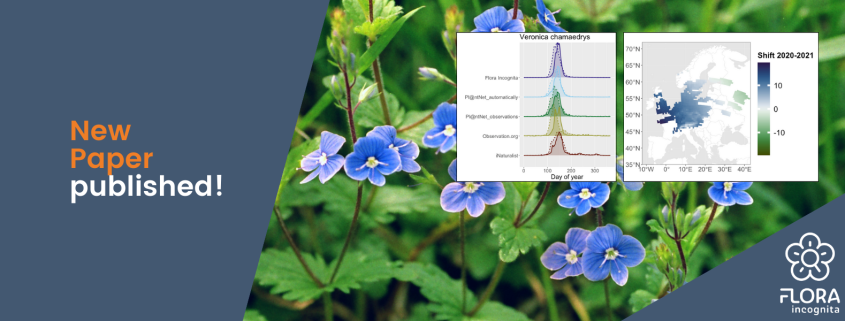
A new study by our research group shows that plant observations collected with identification apps can provide information about the developmental stages of plants – both on a small scale and across Europe. [Read the paper]
Why is it important to document phenology?
Many plants in temperate climates go through a cycle of flowering, leaf emergence, fruiting, leaf colouration and leaf fall every year. This process is called phenology and is strongly influenced by local climatic conditions (for example, the number of days per year on which a certain minimum temperature required for growth is reached; see “Growing Degree Day” or GDD). It is, therefore, not surprising that climate change has a substantial impact on phenology. For example, spring begins earlier than it did in the 1950s, meaning the growing season starts much earlier than it did back then. Such changes impact agricultural processes and can also lead to ecological imbalances. For example, plants begin to flower even before their pollinators are active. However, not all plants react equally to climatic changes. Species with a broader tolerance range for warm days, or where other factors determine phenology, are virtually unaffected by shifts. To gain a truly accurate understanding of the influence of climate on plant phenology, it is essential to document the phenology of as many different species as possible, in different countries and geographical regions.
How does phenological monitoring work?
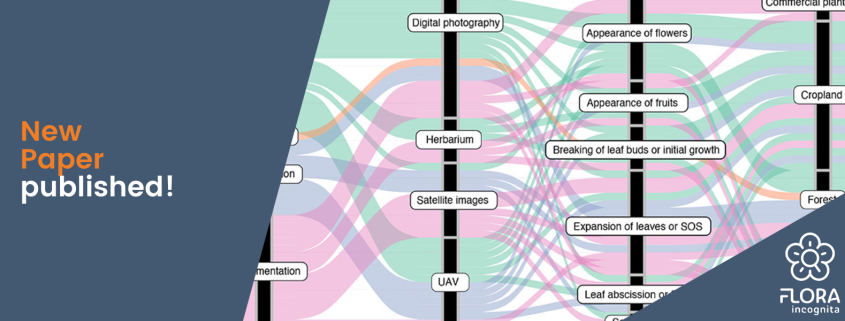
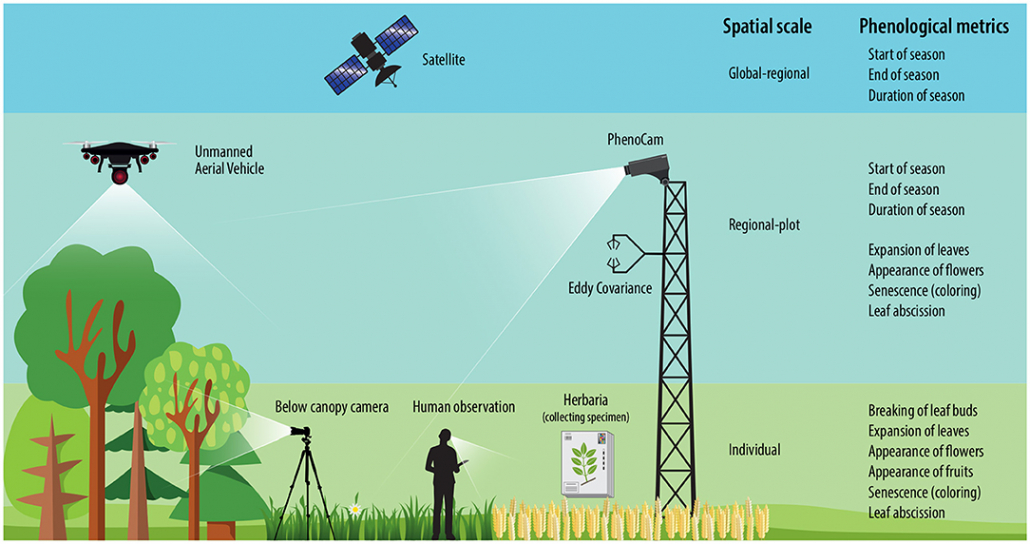
Phenology is already being documented using various methods. Satellite images recognize the greening of entire areas, and cameras in treetops produce automated image series on the condition of the vegetation layer below. Such data sets allow statements to be made about large scales, but hardly allow any conclusions to be drawn about the phenology of individual species or even individuals. For this purpose, there are initiatives that are carried out with the help of trained volunteers. However, the number of these citizen scientists is constantly decreasing, and this type of data collection is usually limited to certain plant species (often trees), countries, or even smaller regions.
Is it possible to document phenology with Flora Incognita?
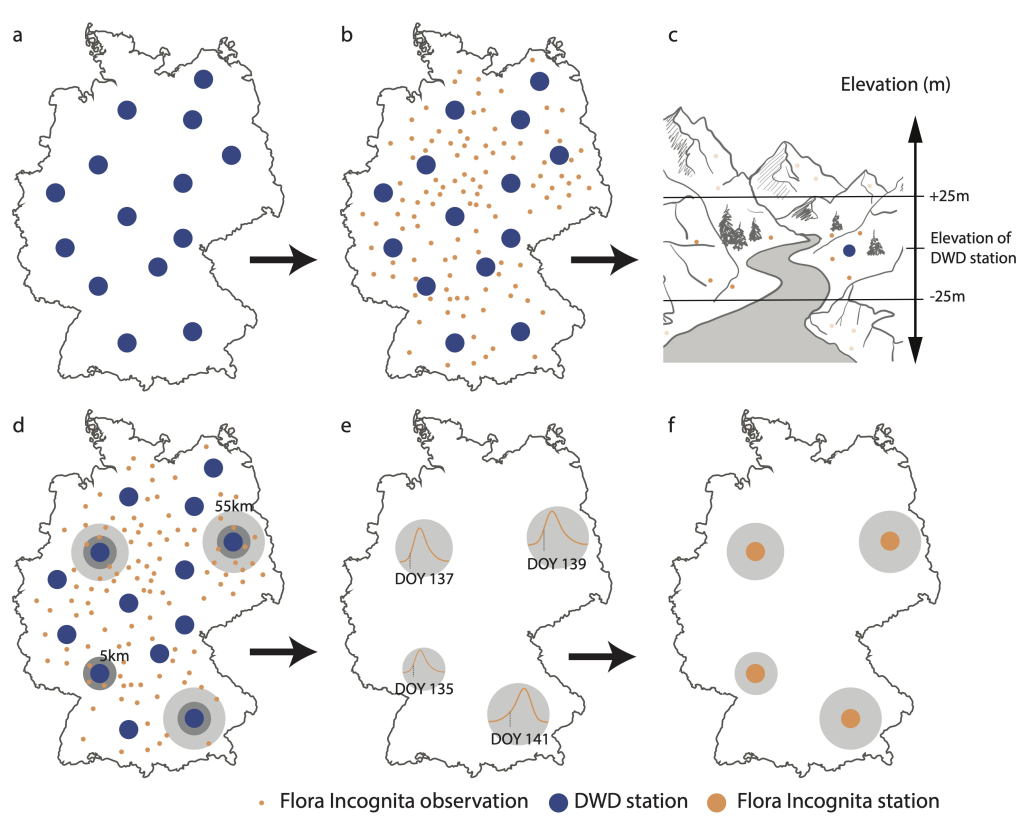
Data collected via plant identification apps such as Flora Incognita can be a solution. The scientists in our project already proved this in 2023: Plants are primarily noticed and photographed when they are conspicuous and also flower, bear colorful fruit, or autumn leaves. This results in observation patterns that indicate phenological events. These patterns often coincide with those published by the German Weather Service (DWD) concerning the onset of flowering species in Germany. Assuming that the DWD registers an earlier start of flowering of the elderberry in one year than in the previous year, this shift is also reflected in the identification requests from Flora Incognita.
Details of this study can be found in this article: Phenology monitoring with Flora Incognita plant observations.
A new study shows phenologies and bioclimatic correlations across Europe
Our new publication now shows that smartphone observations even reflect known supra-regional phenological patterns, such as
- the later flowering of many species in Northern and Eastern Europe or
- the later flowering of many species at higher altitudes, but also
- a Europe-wide shift in the start of flowering between years, as has already been proven for Germany.
This proves that the data generated by plant identification apps is a reliable source for the occurrence of plants at a specific time and place and is well suited for answering further research questions – even on a larger scale.
The results of the study at a glance
Plants are more likely to flower when there are more warm days
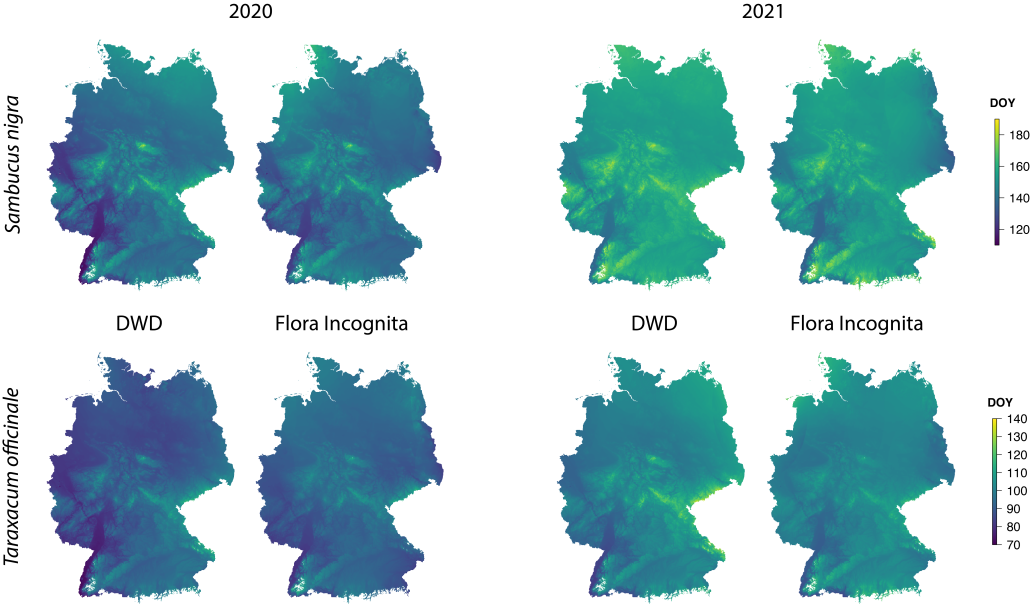
We compared the Europe-wide observation data (sources: Flora Incognita and reporting platforms such as iNaturalist) from 2020 and 2021 for 20 different plant species. We found that spring-flowering plants in particular, such as the gamander speedwell Veronica chamaedrys, flowered earlier in 2020 – up to two weeks earlier than in 2021.
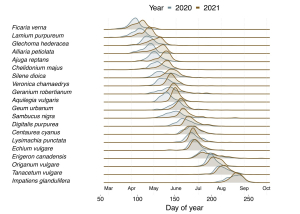
An analysis of the temperature at each location showed that there were significantly more days in spring 2020 on which an average of 5°C or more was reached, meaning that the plants could absorb more heat in a shorter period of time. The effect was less pronounced for species that flower later in the year, such as the tansy Tanacetum vulgare or the common viper’s bugloss Echium vulgare.
Plants flower later if they grow at higher altitudes, further east or north.
However, patterns could be recognized not only between the years but also between different regions. It is known that the same species flowers at different times depending on the location. (-> Hopkins’ bioclimatic law) For example, if the same plant species occurs in Sweden and Spain, the Spanish plant will flower a few days or even weeks earlier than the one in the north. The exact days until flowering naturally vary depending on the plant species. This regularity can also be illustrated with Flora Incognita data:
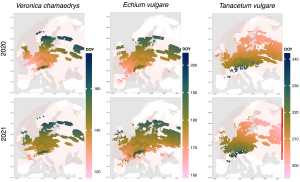
This figure shows the median of the observation data for the three plant species already presented. Pink and orange indicate that the species flowered early in the year at the respective location, while the same species flowered later at another location (coded dark green and blue). The longitudes and latitudes are clearly differentiated, as well as the low and high mountain ranges. Details of the data and methods used can be found in the publication linked at the end of the article.
All 20 plant species analyzed could be classified into one of three main patterns, illustrated here as examples. Veronica chamaedrys shows more reddish colours in 2020 than in 2021; as already mentioned, this is due to the warmer temperatures in spring 2020. Echium vulgare shows only minor responses to different climatic conditions over the years. For Tanacetum vulgare, we found that phenology shows an inverse pattern compared to the other species: Tansy is more likely to flower in eastern, northern, and high altitudes than its siblings in western, southern, and lower-lying parts of Europe. This phenomenon has also been described in the scientific literature. Species that need many warm days to flower have adapted to cold locations by shortening their vegetation period and flowering earlier.
Summary
For the first time, the new publication shows temporal and spatial shifts in plant phenology on a Europe-wide scale using data not collected explicitly for this purpose. For the users of Flora Incognita, this means that each individual plant identification satisfies more than just their curiosity. By documenting plant occurrences at a specific time in a particular place, they create a growing and robust data source on phenology that knows no national borders, includes new species, and can answer numerous further research questions.
Thank you for your curiosity.
The new publication is now freely available:
Rzanny, M., Mäder, P., Wittich, H.C. et al. Opportunistic plant observations reveal spatial and temporal gradients in phenology. npj biodivers 3, 5 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-024-00037-7
Veronica chamaedrys in the title image was captured by Ilse Schönfelder.





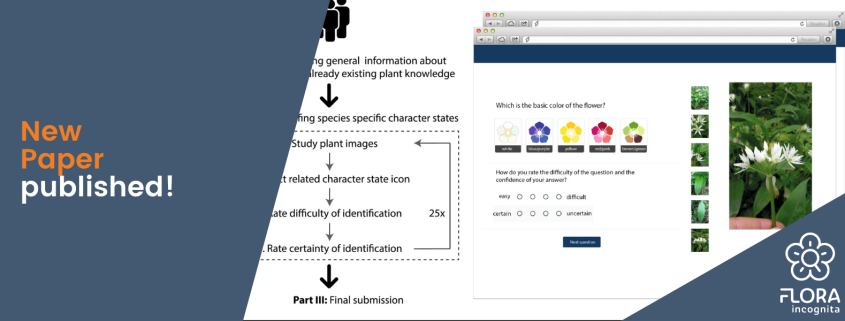


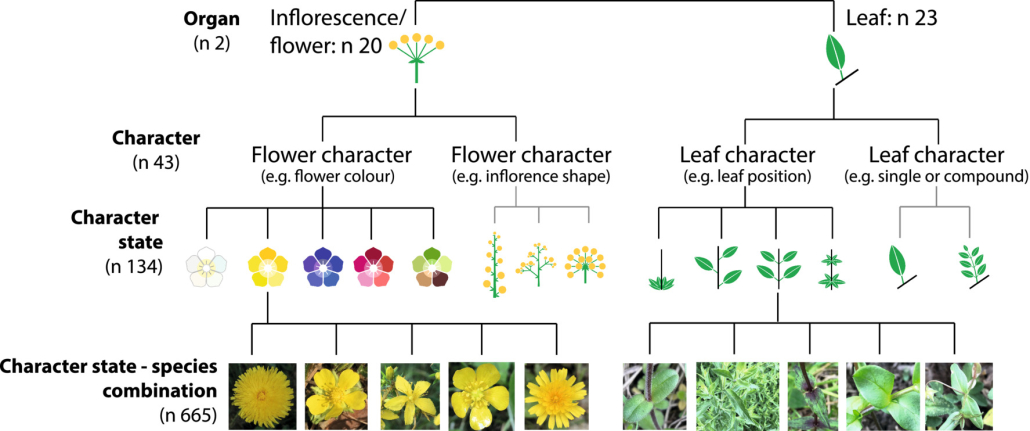
 uish the grass species. All images were taken with different smartphones.
uish the grass species. All images were taken with different smartphones.
 ional Youth Science Competition. Would you have imagined that happening when you started the project?
ional Youth Science Competition. Would you have imagined that happening when you started the project?